Introduction to Demodulation
- Demodulation is getting the initial form of information modulated signal.
- To recoup the data from a modulator, signal a demodulator signal circuit is available in usage.
- There are different types of demodulators as well.
- The demodulator output signal may be described as audio, binary data, or photos.
- 1) What is Demodulation?
- 2) Detection or demodulation
- 3) AM demodulation methods
- 4) Diode rectifier envelope detector
- 5) Product detector
- 6) Synchronous detection
- 7) FM demodulation techniques
- 8) Slope detection
- 9) Ratio detector
- 10) MCQs about Demodulation
- 11) Summary: Demodulation
- 12) You may also like to learn:
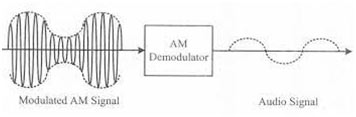
What is Demodulation?
The process of separating the original information or signal from the Modulated-carrier signal. When it comes to amplitude or frequency modulation it entails a tool, called a demodulator or detector, which produces a signal corresponding to the instantaneous changes in amplitude or frequency, respectively.

This signal corresponds to the original modulating signal. In radio transmission, this process is a significant feature of a Receiver, in order to obtain the desired signal.
Detection or demodulation
The terms detection and demodulation are frequently utilized when referring to the general demodulation procedure. Basically, the terms describe the same process, and also the same circuits. As the name shows the demodulation procedure is the reverse of modulation, where a signal such as an audio signal is applied to a carrier signal.
AM demodulation methods
There are a variety of techniques that can be utilized to demodulate AM signals. Various types are utilized in different applications to fit their performance as well as expense.
Diode rectifier envelope detector
This form of detector is the most basic kind, only requiring a single diode and a number of various other low-cost parts. The performance suffices for inexpensive AM broadcast radios, yet it does not fulfill the standards of various other forms of demodulation.
Product detector
It is feasible to demodulate amplitude-regulated signals with a receiver that integrates a product detector of the mixer and a local beat frequency oscillator or carrier injecting oscillator. In its fundamental form, the local oscillator is not synchronized to the incoming signal carrier.
Synchronous detection
The synchronous detector or demodulator is effectively a development of the product detector circuit as well as it, therefore, supplies the maximum efficiency for the demodulation of AM signals.
It uses much more parts than a simple diode detector, yet because of the uptake of incorporated circuit modern technology, it is really simple to include this form of demodulator into several radio receivers for nearly zero incremental expense.
FM demodulation techniques
The main types of FM demodulator found in broadcast receivers, radio communication systems two-way radios or walkie talkies/ handheld radios, etc.,
Slope detection
This is a very simple and basic type of FM demodulation and also it relies upon the selectivity of the receiver itself to provide the demodulation. It is not especially reliable and also is not made use of other than when the receiver does not have an FM capability.
Ratio detector
This sort of detector was one that was extensively made use of when discrete parts were utilized in transistor radios. The ratio detector was required for making use of a transformer that had a third winding to generate an added signal which was stage shifted for the demodulation procedure.
The ratio detector utilized two diodes in addition to a couple of resistors and also capacitors.
- These FM demodulators are utilized in different applications. The various types of FM demodulators give designers an option of techniques relying on the application: broadcast, two-way radio communications, high requirements communications receivers, and so on.
MCQs about Demodulation
- Question 1: What does demodulation refer to?
- A) Modifying the original information signal
- B) Separating the original information from the modulated-carrier signal
- C) Combining multiple signals into one
- D) Amplifying the modulated signal
- Answer: B) Separating the original information from the modulated-carrier signal
- Question 2: Which tool is used for demodulation in amplitude or frequency modulation?
- A) Amplifier
- B) Modulator
- C) Demodulator or detector
- D) Oscillator
- Answer: C) Demodulator or detector
- Question 3: What is the significance of demodulation in radio transmission?
- A) It amplifies the signal.
- B) It produces a signal corresponding to the instantaneous changes in amplitude.
- C) It separates the desired signal from the modulated-carrier signal.
- D) It generates multiple signals from one carrier.
- Answer: C) It separates the desired signal from the modulated-carrier signal.
- Question 4: What is another term frequently used interchangeably with demodulation?
- A) Modulation
- B) Amplification
- C) Detection
- D) Rectification
- Answer: C) Detection
- Question 5: Which demodulation method is the most basic and inexpensive for AM broadcast radios?
- A) Product detector
- B) Synchronous detection
- C) Slope detection
- D) Diode rectifier envelope detector
- Answer: D) Diode rectifier envelope detector
- Question 6: What is the primary component required for a diode rectifier envelope detector?
- A) Transformer
- B) Capacitor
- C) Resistor
- D) Diode
- Answer: D) Diode
- Question 7: Which FM demodulation technique relies on the selectivity of the receiver for demodulation?
- A) Slope detection
- B) Synchronous detection
- C) Product detector
- D) Ratio detector
- Answer: A) Slope detection
- Question 8: What is the key advantage of the synchronous detector for AM demodulation?
- A) Low cost
- B) High efficiency
- C) Simple circuitry
- D) Limited use of components
- Answer: B) High efficiency
- Question 9: In which type of application is the ratio detector commonly used?
- A) Broadcast receivers
- B) Two-way radio communications
- C) High standards communications receivers
- D) AM demodulation
- Answer: A) Broadcast receivers
- Question 10: What are the primary components used in a ratio detector?
- A) Capacitors and resistors
- B) Inductors and diodes
- C) Diodes and resistors
- D) Transistors and capacitors
- Answer: C) Diodes and resistors
- Question 11: Which component is essential for demodulation in amplitude modulation?
- A) Transistor
- B) Capacitor
- C) Demodulator or detector
- D) Inductor
- Answer: C) Demodulator or detector
- Question 12: What is the primary purpose of demodulation?
- A) To amplify the modulated signal
- B) To combine multiple signals into one
- C) To separate the original information from the carrier signal
- D) To generate multiple signals from one carrier
- Answer: C) To separate the original information from the carrier signal
- Question 13: Which demodulation method relies on the phase shift of the signal?
- A) Synchronous detection
- B) Slope detection
- C) Product detector
- D) Ratio detector
- Answer: A) Synchronous detection
- Question 14: What is the primary function of a diode rectifier envelope detector?
- A) To amplify the signal
- B) To produce a high-frequency signal
- C) To separate the envelope of the modulated signal
- D) To generate a carrier signal
- Answer: C) To separate the envelope of the modulated signal
- Question 15: Which demodulation method is commonly used when the receiver lacks FM capability?
- A) Ratio detector
- B) Synchronous detection
- C) Slope detection
- D) Product detector
- Answer: C) Slope detection
- Question 16: In FM demodulation, which technique relies on the receiver’s selectivity?
- A) Slope detection
- B) Synchronous detection
- C) Product detector
- D) Ratio detector
- Answer: A) Slope detection
- Question 17: Which demodulation method provides maximum efficiency for AM signals?
- A) Slope detection
- B) Synchronous detection
- C) Product detector
- D) Ratio detector
- Answer: B) Synchronous detection
- Question 18: What is the key advantage of using a product detector for demodulation?
- A) Low cost
- B) High efficiency
- C) Simplicity of circuitry
- D) Wide frequency range
- Answer: B) High efficiency
- Question 19: Which application commonly uses a ratio detector for demodulation?
- A) Television receivers
- B) Broadcast receivers
- C) Radar systems
- D) FM radios
- Answer: B) Broadcast receivers
- Question 20: What is the primary function of demodulation in communication systems?
- A) To amplify the received signal
- B) To extract the original information from the modulated signal
- C) To generate a carrier signal
- D) To combine multiple signals into one
- Answer: B) To extract the original information from the modulated signal
Summary: Demodulation
Demodulation is the process of extracting the original information or signal from a modulated carrier signal. It is a crucial aspect of communication systems, enabling the recovery of transmitted data. This tutorial provides an overview of demodulation, including its definition, significance, and various techniques used in amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM).
In the introduction, demodulation is described as the retrieval of the initial form of the modulated signal, whether it be audio, binary data, or visual content. The tutorial emphasizes the importance of demodulation in obtaining the desired signal in radio transmission and other communication systems.
The tutorial further explains the distinction between detection and demodulation, highlighting their interchangeable usage and the reverse relationship they share with modulation.
For AM demodulation, several methods are discussed, including the diode rectifier envelope detector, product detector, and synchronous detection. Each method is described in terms of its simplicity, performance, and suitability for different applications.
In the section on FM demodulation techniques, the tutorial covers slope detection and ratio detector methods. These techniques are explained with regard to their reliance on receiver selectivity and their historical significance in transistor radios.
Overall, the tutorial provides a comprehensive overview of demodulation, its methods, and its significance in communication systems. It serves as a valuable resource for understanding the process of signal extraction in various modulation schemes.
