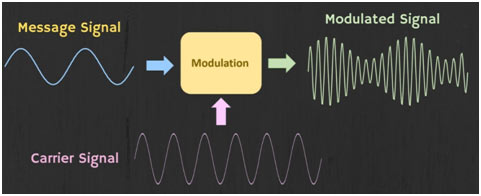
Modulation
The picture by TV, sound, and speech are transmitted over hundreds of kilometers by radio transmitters. The message signal due to its low signal strength cannot travel long distances plus there are other factors such as external noise, friction, long-distance which also reduce the signal strength.
In these cases, the carrier of speech and pictures are high-frequency radio waves. The information is superposed on the radio wave. It carries along with it to its destination.
Definition:
The process of combining low-frequency signals with high-frequency radio waves is called modulation. The waveform as a result is called a modulated carrier wave.
Carrier Wave: High-frequency radio wave with high energy in modulation.
Modulation Signal: the low-frequency signal in modulation.
Types of Signals in Modulation
There are three types of signals in modulation used to send messages from source to destination.
Message Signal
The signal having a message to be transmitted from source to destination is a message signal. It is also called modulating or baseband signal.
Carrier Signal
It is the high frequency and high energy signal which carries no information. It has characteristics like amplification, frequency to carry modulating signal from transmitter to receiver.
Modulated Signal
When the low signal and high-frequency signal combined, the resultant signal formed is called modulated signal.
Types of Modulation
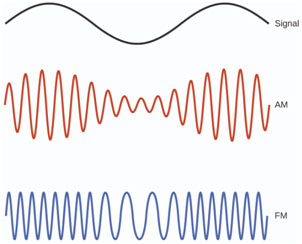
Amplitude Modulation (A.M)
In this process of modulation amplitude of carrier wave changes according to the signal that is the amplitude of carrier waves changes in amplitude modulation. When there is no signal, the amplitude of the carrier wave is equal to the modulated amplitude but when the signal is present the amplitude of the carrier modifies according to the inconstant value of the signal.
During the positive half cycle of the signal amplitude of the carrier increase to the sum of the amplitude of carrier and signal. During the negative half cycle of the signal amplitude of the carrier increases and becomes equal to the amplitude carrier and the signal.
The transmission frequency ranges from 540 kHz to 1600 kHz.
Advantage
- They are better to send the signal for large ranges.
Disadvantage
- These have poor quality transmission of sound.
Applications
- Broadcast transmissions: AM is still extensively used for transmitting on the long, medium, and short-wave bands.
- Airband radio: VHF transmissions for numerous airborne applications still use AM.
Frequency Modulation (F.M)
Frequency modulation is a type of modulation where the information (message signal) is transmitted over a carrier wave by varying its frequency according to the amplitude of the message signal.
In frequency modulation, the amount of change in frequency of the carrier signal is determined by the amplitude of the message signal. The frequency of the modulated wave is high when the message signal reaches its maximum amplitude.
The carrier wave does not carry any information so even if we alter the frequency of the carrier wave, there will be no information loss. Nevertheless, if we change the frequency of the modulating signal, some amount of information loss will happen due to the fact that the modulating signal contains the information. So, the frequency of the modulating signal should not be changed.
The transmission frequency ranges from 88MHz to 108MHz.
Advantage
- These are less impacted by electrical interference than AM waves.
- Offers higher quality transmission of sound.
Downside
- They are less able to travel around obstacles such as high structures, buildings and hills.
- It needs broader bandwidth than amplitude modulation.
Applications
- FM broadcasting
- Radar
- Magnetic tape-recording systems
Phase modulation
Phase modulation (PM), in which the phase of the carrier wave is varied to reflect changes in the frequency of the information. In PM, the frequency is unchanged while the phase is altered relative to the base carrier frequency. It is similar to FM.
Polarization modulation
Polarization modulation, in which the angle of rotation of an optical carrier signal is varied to reflect transmitted data.
Pulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation, in which an analog signal is sampled to obtain a data stream that is used to modulate a digital carrier signal.
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), which uses two AM providers to encode 2 or more bits in a single transmission.
Importance of Modulation
The message signal is low strength signal so cannot travel long distance. The carrier wave cannot carry information. In order to send data in form of audio, pictures, or other forms, the message signal is superimposed on a high-frequency carrier wave and this process is modulation. By modulation, data can easily be transmitted over long distances without loss.
MCQs about Modulation
- What is modulation?
- A. Combining high-frequency radio waves with low-frequency signals
- B. Separating high-frequency radio waves from low-frequency signals
- C. Amplifying high-frequency radio waves
- D. Reducing the frequency of radio waves
- Answer: A. Combining high-frequency radio waves with low-frequency signals
- Which signal carries the actual information to be transmitted in modulation?
- A. Carrier signal
- B. Modulated signal
- C. Message signal
- D. Amplified signal
- Answer: C. Message signal
- What is the purpose of the carrier signal in modulation?
- A. To carry the modulated signal
- B. To amplify the message signal
- C. To provide energy to the modulated signal
- D. To carry the actual information
- Answer: C. To provide energy to the modulated signal
- Which type of modulation changes the amplitude of the carrier wave according to the signal?
- A. Amplitude Modulation (A.M)
- B. Frequency Modulation (F.M)
- C. Phase modulation
- D. Polarization modulation
- Answer: A. Amplitude Modulation (A.M)
- What is the transmission frequency range for Amplitude Modulation (A.M)?
- A. 88MHz to 108MHz
- B. 540 kHz to 1600 kHz
- C. 20 kHz to 20 MHz
- D. 3 kHz to 300 kHz
- Answer: B. 540 kHz to 1600 kHz
- Which application extensively uses Amplitude Modulation (A.M) for transmission?
- A. FM broadcasting
- B. Magnetic tape-recording systems
- C. Broadcast transmissions
- D. Radar
- Answer: C. Broadcast transmissions
- What type of modulation offers higher quality transmission of sound?
- A. Amplitude Modulation (A.M)
- B. Frequency Modulation (F.M)
- C. Phase modulation
- D. Polarization modulation
- Answer: B. Frequency Modulation (F.M)
- What is the transmission frequency range for Frequency Modulation (F.M)?
- A. 88MHz to 108MHz
- B. 540 kHz to 1600 kHz
- C. 20 kHz to 20 MHz
- D. 3 kHz to 300 kHz
- Answer: C. 20 kHz to 20 MHz
- Which application is NOT listed as an application of Frequency Modulation (F.M)?
- A. FM broadcasting
- B. Radar
- C. Magnetic tape-recording systems
- D. Airband radio
- Answer: D. Airband radio
- What type of modulation involves varying the phase of the carrier wave to reflect changes in frequency?
- A. Phase modulation
- B. Polarization modulation
- C. Pulse-code modulation
- D. Quadrature amplitude modulation
- Answer: A. Phase modulation
- What is the modulation type in which the angle of rotation of an optical carrier signal is varied?
- A. Phase modulation
- B. Polarization modulation
- C. Pulse-code modulation
- D. Quadrature amplitude modulation
- Answer: B. Polarization modulation
- Which modulation technique involves sampling an analog signal to obtain a data stream?
- A. Phase modulation
- B. Polarization modulation
- C. Pulse-code modulation
- D. Quadrature amplitude modulation
- Answer: C. Pulse-code modulation
- What is Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) used for?
- A. Encoding analog signals
- B. Encoding digital signals
- C. Encoding frequency signals
- D. Encoding phase signals
- Answer: B. Encoding digital signals
- Why is modulation important?
- A. To increase the strength of the message signal
- B. To decrease the frequency of the carrier wave
- C. To transmit data over long distances without loss
- D. To amplify the carrier signal
- Answer: C. To transmit data over long distances without loss
- Which modulation technique involves changing the amplitude of the carrier wave according to the signal?
- A. Amplitude Modulation (A.M)
- B. Frequency Modulation (F.M)
- C. Phase modulation
- D. Pulse-code modulation
- Answer: A. Amplitude Modulation (A.M)
- In Amplitude Modulation (A.M), what happens to the amplitude of the carrier wave during the positive half cycle of the signal?
- A. It decreases to zero.
- B. It remains constant.
- C. It increases to the sum of the carrier amplitude and signal amplitude.
- D. It becomes negative.
- Answer: C. It increases to the sum of the carrier amplitude and signal amplitude.
- Which modulation technique offers higher quality transmission of sound?
- A. Amplitude Modulation (A.M)
- B. Frequency Modulation (F.M)
- C. Phase modulation
- D. Quadrature amplitude modulation
- Answer: B. Frequency Modulation (F.M)
- What is the range of transmission frequency for Frequency Modulation (F.M)?
- A. 540 kHz to 1600 kHz
- B. 20 kHz to 20 MHz
- C. 88MHz to 108MHz
- D. 3 kHz to 300 kHz
- Answer: B. 20 kHz to 20 MHz
- Which modulation technique involves varying the phase of the carrier wave relative to the base carrier frequency?
- A. Phase modulation
- B. Polarization modulation
- C. Pulse-code modulation
- D. Quadrature amplitude modulation
- Answer: A. Phase modulation
Wrapping up
In summary, modulation is the process of combining low-frequency signals with high-frequency radio waves, resulting in a modulated carrier wave. This technique allows for the transmission of data, such as TV, sound, and speech, over long distances by superposing information onto high-frequency radio waves. There are three types of signals involved in modulation: the message signal containing the information, the carrier signal which carries no information but provides energy, and the modulated signal formed by combining the message and carrier signals.
Various types of modulation techniques exist, including Amplitude Modulation (A.M), Frequency Modulation (F.M), Phase modulation, Polarization modulation, Pulse-code modulation, and Quadrature amplitude modulation. Each technique has its advantages, disadvantages, and applications, ranging from broadcast transmissions to radar systems.
The importance of modulation lies in its ability to facilitate the transmission of data over long distances without loss. By superimposing the low-strength message signal onto a high-frequency carrier wave, modulation ensures efficient communication of audio, pictures, and other forms of data.