Pathogenic bacteria are organisms that can cause disease. This short article deals with human pathogenic bacteria.
Bacterial Infection
A bacterial infection is an expansion of a harmful strain of bacteria on or inside the body. Bacteria can infect any part of the body. Pneumonia, meningitis, and food poisoning are simply a couple of diseases that might be triggered by harmful bacteria.
Cholera
Cholera is a bacterial illness normally spread out through contaminated water. Cholera causes extreme diarrhea and dehydration. Left neglected, cholera can be fatal within hours, even in formerly healthy individuals.
Causes
A bacterium called Vibrio cholerae triggers cholera infection. Contaminated public wells are frequent sources of massive cholera breakouts. Individuals living in crowded conditions without adequate sanitation are specifically at risk.
Symptoms
Cholera-related diarrhea comes on unexpectedly and can quickly cause hazardous fluid loss. It can also include queasiness and vomiting and dehydration.
Prevention
Cholera can be prevented by cleaning hands with soap and water often and by consuming safe and clean water only.
Typhoid
Typhoid is a bacterial infection that can result in high fever, diarrhea, and vomiting. It can be fatal. The bacterium resides in the intestinal tracts and bloodstream of people. It spreads out in between individuals by direct contact with the faeces of a contaminated person.
Cause
Typhoid is an infection brought on by the bacterium Salmonella typhimurium (S. Typhi).
Symptoms
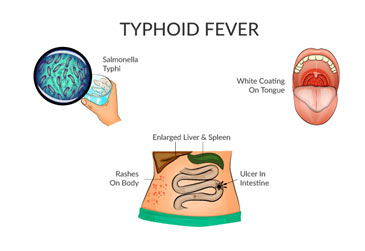
The two significant signs of typhoid are fever and rash. Typhoid fever is especially high, gradually increasing over a number of days to approximately 104 degrees Fahrenheit or 39 to 40 degrees Celsius. The rash, which does not affect every patient, includes rose-colored areas, especially on the neck and abdomen.
Treatment
The only effective treatment for typhoid is antibiotics. Other than prescription antibiotics, it is necessary to rehydrate by consuming sufficient water.
Campylobacteriosis
In humans, campylobacteriosis is the chief kind of food poisoning.
Causes
Most Campylobacter infections are probably gotten by eating raw or undercooked poultry or eating something that touched it. Campylobacter is likewise transferred by other foods, including seafood, meat, and produce; by contact with animals; and by drinking contaminated water.
Symptoms
Individuals with Campylobacter infection typically have diarrhea (typically bloody), fever, and stomach cramps. Queasiness and vomiting might accompany diarrhea. These signs generally start 2 to 5 days after the individual ingests Campylobacter and lasts about one week.
Treatment
It can be dealt with antibiotics recommended by doctors.
Tetanus
Tetanus, also called lockjaw, is a major infection in which bacteria produce a toxin that impacts the brain and nerve system, resulting in stiffness in the muscles.
Causes
Tetanus is caused by the Clostridium tetani bacterium. When Clostridium tetani enter the body, they multiply quickly and release tetanospasmin, a neurotoxin. When tetanospasmin gets in the bloodstream, it quickly spreads around the body, triggering tetanus symptoms.
Symptoms
Tetanus signs usually emerge about 7 to 10 days after the initial infection. Muscle signs include spasms and stiffness. Stiffness normally begins with the chewing muscles, hence the name lockjaw. Breathing problems might result from neck and chest muscle stiffness. In some individuals, stomach and limb muscles are likewise impacted.
Treatment
Any cut or wound should be completely cleaned up to prevent infection. A tetanus-prone injury should be treated by a doctor immediately. Any patient with a serious injury must receive tetanus immunoglobulin (TIG) as soon as possible, even if they have actually been vaccinated. Tetanus immunoglobulin contains antibodies that eliminate Clostridium tetani. It is injected into a vein and supplies instant short-term protection against tetanus.
Bacterial Skin Infections
Bacterial skin infections are normally brought on by gram-positive strains of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus or other organisms. Typical bacterial skin infections include:
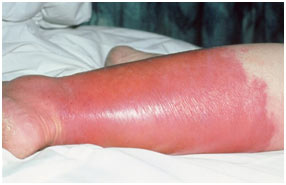
Cellulitis causes an agonizing, red infection that is typically warm to the touch. Cellulitis occurs most often on the legs; however, it can appear anywhere on the body.
Boils are deep skin infections that start in hair roots. Boils are firm, red, tender bumps that advance up until pus accumulates beneath the skin.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: what physical agents are used to controlling bacteria?
Ans: Sterilization is a process used to kill remove or control microorganisms like bacteria.
Q2: Which bacterium culture was isolated and by whom?
Ans: Louis Pasteur isolated the bacterium of Chicken cholera in the 1880s.
Q3: What do attenuated bacteria do to host?
Ans: Attenuated bacteria can stimulate the host to produce antibodies.
Q4: What kind of radiation are useful for killing microbes?
Ans: Electromagnetic radiations with wavelengths below 300 nm are effective in killing microbes and bacteria.
Q5: What are antibiotics?
Ans: These are the chemotherapeutic drugs which are used to kill or control the growth of bacteria. It can be obtained from some useful bacteria, fungi and can also be prepared in laboratories.