Definition
Radioactivity is the phenomenon of the spontaneous disintegration of unstable atomic nuclei to form more energetically stable atomic nuclei. The elements having a charge number greater than 82 are unstable and emit invisible radiations.
Radioactive decay is a highly exoergic, statistically random, first-order procedure that occurs with a small amount of mass being converted to energy.
History of Radioactivity
The French scientist Henri Becquerel, in 1896, first discovered the phenomenon of radioactivity while working with phosphorescent materials. These materials radiance in the dark after direct exposure to light, and he presumed that the glow produced in cathode ray tubes by X-rays might be associated with phosphorescence.
He found that an ore consisting of Uranium emits invisible radiation which permeates through a black paper wrapping a photographic plate and affects the plate.
In 1898, after Henri Becquerel, Marie Curie and Pierre Curie found two new radioactive elements Polonium and Radium.
Explanation
Radioactivity refers to the particles which are emitted from nuclei as a result of nuclear instability. Due to the fact that the nucleus experiences the intense conflict between the two greatest forces in nature, it should not be surprising that there are numerous nuclear isotopes that are unstable and discharge some sort of radiation.
Measuring of Radioactivity
Radioactive decay rates are typically stated in terms of their half-lives, and the half-life of an offered nuclear species is related to its radiation risk. The various kinds of radioactivity result in various decay courses which transmute the nuclei into other chemical elements. Analyzing the quantities of the decay products makes possible radioactive dating.
Radioactive Particles
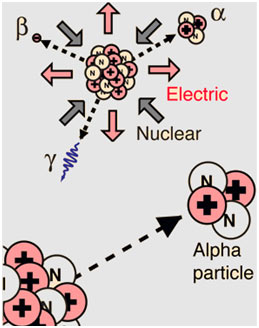
After numerous years of research and study, scientists recognized several unique types of particles arising from radioactive procedures (radiation). The 3 distinct types of radiation were called after the first three letters of the Greek alphabet: (alpha), (beta), and (gamma).
These 3 forms of radiation can be separated by an electromagnetic field given that positively charged alpha particles flex in one direction, negative beta particles flex in an opposite direction, and electrically neutral gamma radiation doesn’t flex at all.
α- particles
They are helium nuclei. Each particle has two protons and 2 neutrons.
charge number Z= 2
mass number A=4
β– particles
They are fast-moving electrons i.e., coming out of the nucleus.
charge number Z= -1
mass number A= 0
γ- Ryas
Like x-rays, γ-rays are also electro-magnetic rays coming out of the nucleus. The wavelength of γ-rays is much shorter than the x-rays. They have a very high frequency.
Advantages of Radioactivity
- Gamma rays can pass deep inside the body, they can be used to exterminate cancer cells and even cure individuals of this health problem and this process of treatment is called radiotherapy.
Even though exposure to large amounts can also cause cancers.
- Gamma rays successfully kill microorganisms that cause food to decay. So, food treated with this radiation has a longer shelf life.
- A Geiger Counter is an instrument that measures radiation. If radioisotopes are added to oil or gas, engineers can follow the radioisotope, and trace any leaks in oil or gas pipes.
- Carbon 14 is used to calculate the age of animal and plant remains by comparing its half-life. This is called carbon dating.
- By measuring the argon content of many rocks that contain potassium, scientists can compute the age of the rock. This is called rock dating.
Disadvantages of Radioactivity
- Direct exposure to large quantities of radioactivity can trigger queasiness, vomiting, loss of hair, diarrhea, hemorrhage, destruction of the digestive lining, central nervous system damage, and death.
- It likewise triggers DNA damage and raises the threat of cancer, particularly in children and fetuses.
- Direct exposure to damaging radiations can cause severe skin and other organs’ cancer.
MCQs
- Which of the following best defines radioactivity?
- A) The emission of light from unstable atomic nuclei
- B) The phenomenon of spontaneous disintegration of unstable atomic nuclei
- C) The generation of energy within stable atomic nuclei
- D) The process of creating radioactive elements artificially
- Answer: B
- Who was the French scientist credited with the discovery of radioactivity?
- A) Albert Einstein
- B) Marie Curie
- C) Henri Becquerel
- D) Isaac Newton
- Answer: C
- In which year did Henri Becquerel discover radioactivity?
- A) 1876
- B) 1889
- C) 1896
- D) 1901
- Answer: C
- Which elements did Marie Curie and Pierre Curie discover as radioactive elements?
- A) Uranium and Thorium
- B) Polonium and Thorium
- C) Polonium and Radium
- D) Uranium and Radium
- Answer: C
- What does the term “half-life” refer to in the context of radioactivity?
- A) The time it takes for half of a radioactive element to decay
- B) The duration of time for which radiation remains active
- C) The period of time required for radioactive decay to occur
- D) The time it takes for a radioactive element to lose all its activity
- Answer: A
- Which of the following is NOT a type of radioactive particle?
- A) δ- particles
- B) α- particles
- C) β– particles
- D) γ- rays
- Answer: A
- What is the charge number (Z) and mass number (A) of α-particles?
- A) Z= -1, A= 0
- B) Z= 1, A= 1
- C) Z= 0, A= 1
- D) Z= 2, A= 4
- Answer: D
- What are β– particles?
- A) Neutrons
- B) Protons
- C) Electrons
- D) Alpha particles
- Answer: C
- Which type of radiation is used in radiotherapy to treat cancer?
- A) α-particles
- B) β– particles
- C) γ- rays
- D) δ- particles
- Answer: C
- What is the advantage of using gamma rays in food preservation?
- A) They enhance food flavor
- B) They promote faster cooking
- C) They increase food shelf life
- D) They decrease food nutritional value
- Answer: C
- Which instrument measures radiation?
- A) Microscope
- B) Geiger Counter
- C) Thermometer
- D) Barometer
- Answer: B
- What is carbon dating used for?
- A) Calculating the age of animal and plant remains
- B) Determining the half-life of carbon isotopes
- C) Measuring the rate of radioactive decay
- D) Assessing the radiation exposure of an area
- Answer: A
- What are the disadvantages of direct exposure to radioactivity?
- A) Enhanced cognitive abilities
- B) Increased resistance to diseases
- C) Risk of DNA damage and cancer
- D) Improved immune system function
- Answer: C
- Which type of radiation has the highest penetration power?
- A) α-particles
- B) β– particles
- C) γ- rays
- D) δ- particles
- Answer: C
- Who discovered Polonium and Radium?
- A) Albert Einstein
- B) Isaac Newton
- C) Marie Curie and Pierre Curie
- D) Henri Becquerel
- Answer: C
- What is the primary cause of radioactive decay?
- A) Decrease in mass
- B) Increase in energy
- C) Instability of atomic nuclei
- D) Generation of visible light
- Answer: C
- How are radioactive decay rates typically expressed?
- A) In terms of their radioactive power
- B) In terms of their radiation intensity
- C) In terms of their half-lives
- D) In terms of their atomic masses
- Answer: C
- What is the charge of α-particles?
- A) Positive
- B) Negative
- C) Neutral
- D) Variable
- Answer: A
Summary:
Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of unstable atomic nuclei, emitting particles in the process. Henri Becquerel’s discovery in 1896 marked the beginning of understanding this phenomenon, further explored by Marie and Pierre Curie who discovered Polonium and Radium.
The emitted particles—α (alpha), β– (beta), and γ (gamma)—have unique properties and can be separated by electromagnetic fields. α-particles are helium nuclei, β– particles are fast-moving electrons, and γ-rays are electromagnetic radiation with a very short wavelength.
Advantages of radioactivity include its use in cancer treatment (radiotherapy), food preservation, leak detection in oil and gas pipes, and dating methods like carbon dating and rock dating. However, exposure to high levels of radioactivity can lead to severe health issues such as nausea, cancer, and DNA damage, highlighting the importance of careful handling and regulation of radioactive materials.

