Law of Gravity and Relation with Newton’s Third Law
The very first man who developed the concept of gravity was Isaac Newton. It was an evening in 1665 when he was trying to solve the secret of why planets revolve around the Sun. Unexpectedly an apple fell from the tree under which he was sitting.
The idea of gravity flashed in his mind. He found not only the reason for falling apple but also the cause that makes the planets to move around the Sun and the moon around the Earth.
The Force of Gravitation
Based on his observations, Newton concluded that the force which triggers an apple to fall on the Earth and the force which keeps the moon in its orbit is of the very same nature.
He further concluded that there exists a force due to which everybody of the universe attracts in every other body. He called this force the force of gravitation.
Law of Gravitation
According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation:
“Everybody in the universe attracts every other body with a force which is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centres.”
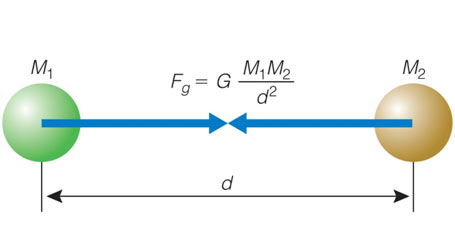
Explanation
Consider two bodies of masses m1 and m2. The distance between the centres of the masses is d.
Mathematical Form
According to the law of gravitation, the gravitational force of attraction F with which the two masses m and m separated by a distance d attract each other can be stated as:
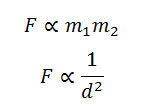
By combining both we get,
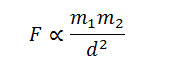
Now by putting constant we get the final equation,
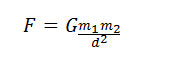
Here G is the proportionality constant. It is called the universal constant of gravitation. Its value is the same all over. In SI units its value is 6.673 x10-11Nm2kg-2.
Due to the little value of G, the gravitational force of attraction between things around us is really small and we do not feel it. Given that the mass of Earth is large, it attracts close-by items with a significant force.
The weight of a thing on the Earth is the result of the gravitational force of attraction between the Earth and the object.
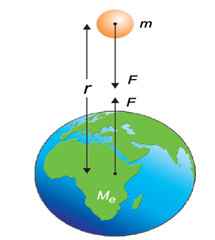
Law of Gravitation and Third Law of Newton
It is to be kept in mind that mass m1attracts in m2 towards it with a force F while mass m2attracts in m1 towards it with a force of the same magnitude F however in opposite direction. If the force acting upon m1 is thought about as action then the force acting upon m2 will be the reaction of that action.
The action and reaction due to the force of gravitation are equivalent in magnitude but opposite in direction. This follows Newton’s 3rd law of motion which specifies, to every action there is always an equivalent but opposite reaction.
MCQs:
- What flashed in Isaac Newton’s mind when an apple fell from a tree in 1665?
- A) The concept of gravity
- B) The concept of motion
- C) The concept of light
- D) The concept of sound
- Answer: A) The concept of gravity
- According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, how does the gravitational force between two bodies depend on their masses?
- A) Directly proportional to the sum of their masses
- B) Directly proportional to the square of their masses
- C) Inversely proportional to the product of their masses
- D) Inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centres
- Answer: B) Directly proportional to the square of their masses
- What does the constant represent in the equation for gravitational force?
- A) Gravitational force
- B) Planck’s constant
- C) Universal constant of gravitation
- D) Earth’s gravitational acceleration
- Answer: C) Universal constant of gravitation
- Why do we not feel the gravitational force between objects around us?
- A) Due to the small mass of Earth
- B) Due to the small value of
- C) Due to the large value of
- D) Due to the large mass of Earth
- Answer: B) Due to the small value of
- What is the result of the gravitational force of attraction between the Earth and an object?
- A) Acceleration of the object
- B) Velocity of the object
- C) Weight of the object
- D) Mass of the object
- Answer: C) Weight of the object
- According to Newton’s third law of motion, how do the action and reaction due to the force of gravitation compare?
- A) They are unequal in magnitude and opposite in direction
- B) They are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
- C) They are unequal in magnitude and same in direction
- D) They are equal in magnitude and same in direction
- Answer: B) They are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
- What does Newton’s third law of motion state?
- A) Every object persists in its state of rest or uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force
- B) The rate of change of momentum of an object is directly proportional to the applied force
- C) For every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction
- D) The gravitational force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
- Answer: C) For every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction
- How did Newton develop the concept of gravity?
- A) By observing the motion of planets
- B) By observing the motion of falling objects
- C) By observing the motion of the moon
- D) By observing the motion of stars
- Answer: B) By observing the motion of falling objects
- What keeps the moon in its orbit according to Newton’s observations?
- A) Gravitational force
- B) Magnetic force
- C) Electric force
- D) Centripetal force
- Answer: A) Gravitational force
- What does the law of universal gravitation state?
- A) Every body attracts every other body with a force directly proportional to their masses
- B) Every body attracts every other body with a force inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centres
- C) Every body attracts every other body with a force inversely proportional to their masses
- D) Every body attracts every other body with a force directly proportional to the square of the distance between their centres
- Answer: B) Every body attracts every other body with a force inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centres
- What conclusion did Newton draw about the force that triggers an apple to fall and the force that keeps the moon in its orbit?
- A) They are unrelated
- B) They are of different natures
- C) They are of the same nature
- D) They are equal in magnitude
- Answer: C) They are of the same nature
- What is the value of the universal constant of gravitation in SI units?
- A) 9.8 m/s2
- B) 3.00×108 m/s
- C) 6.673×10−11 N m2kg−2
- D) 1.38×10−23 J/K
- Answer: C) 6.673×10−11 N m2kg−2
- How does the law of gravitation relate to Newton’s third law of motion?
- A) They are unrelated
- B) They contradict each other
- C) They are equivalent statements
- D) They are independent concepts
- Answer: C) They are equivalent statements
- What do the forces acting between two masses according to Newton’s law of gravitation represent?
- A) They represent action only
- B) They represent reaction only
- C) They represent both action and reaction
- D) They represent neither action nor reaction
- Answer: C) They represent both action and reaction
Summary:
Isaac Newton’s groundbreaking discoveries in gravity reshaped our understanding of the universe. His observations, including the falling of an apple, led to the formulation of the law of universal gravitation.
According to this law, every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This force of gravitation, represented by Newton’s third law of motion, acts equally on both bodies, illustrating the principle of action and reaction.
The universal constant of gravitation, denoted by , quantifies this force and remains consistent throughout the universe. Despite its small value, the gravitational force of attraction between celestial bodies is immense, governing planetary orbits and determining the weight of objects on Earth.
Newton’s profound insights into gravity continue to underpin our understanding of fundamental physics.

