Statement
The momentum of an isolated system of two or more than two interacting bodies remains constant.
Description
Momentum of a system depends upon its mass and velocity. A system is a group of bodies within certain borders. An isolated system is a group of bodies interacting witch each other on which no external force is acting. If no unbalanced or net force acts upon a system, then its momentum remains consistent. Thus, the momentum of an isolated system is constantly conserved.
Mathematical Expression
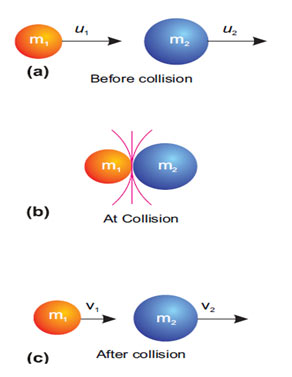
Let consider an isolated system of two spheres of masses m1 and m2. They are moving in a straight line with initial velocities u1 and u2 respectively, such that u1 is greater than u2. The sphere of mass m1 approaches the sphere of mass m2 as they move.
- Initial momentum of mass m1 = m1u1
- Initial momentum of mass m2 = m2u2
- The overall initial momentum of the system before collision = m1u1 +m2u2.
After at some point mass m1 strikes m2 with some force. According to Newton’s third law of motion, m2 applies an equivalent and opposite reacting force on m1. Let their speeds end up being v1 and v2 respectively after a collision. Then
- Final momentum of mass m1 = m1v1.
- Final momentum of mass m2 = m2v2.
- Overall final momentum of the system after collision = m1v1 +m2v2.
According to the law of conservation of momentum
Total initial momentum of the system before collision = Total final momentum of the system after the collision.
m1u1 + m2u2= +m1v1 + m2v2
Example of Law of Conservation of Momentum
Consider a system of gun and a bullet. Before firing the gun, both the gun and bullet are at rest, so the total momentum of the system is absolutely zero. As the gun is fired, bullet shoots out of the gun and obtains momentum. To conserve the momentum of the system, the gun recoils.
According to the law of conservation of momentum, the total momentum of the gun and the bullet will likewise be absolutely zero after the gun is fired.
Let m be the mass of the bullet and v be its speed on firing the gun; M be the mass of the gun and V be the velocity with which it recoils. Therefore, the overall momentum of the gun and the bullet after the gun is fired will be;
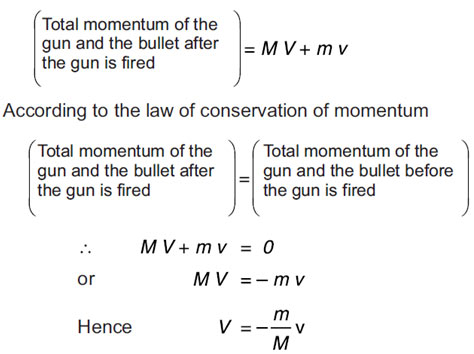
A negative mark indicates that the speed of the gun is opposite to the speed of the bullet, i.e., the gun recoils. Since the mass of the gun is much larger than the bullet, for that reason, the recoil is much smaller than the speed of the bullet.
Rockets and jet engines also work on the exact same principle. In these makers, hot gases produced by the burning of fuel rush out with large momentum. The machines acquire an equivalent and opposite momentum. This enables them to move with really high speeds.
MCQs:
- What does the Law of Conservation of Momentum state?
- A) Momentum increases in an isolated system
- B) Momentum decreases in an isolated system
- C) Momentum remains constant in an isolated system
- D) Momentum varies randomly in an isolated system
- Answer: C) Momentum remains constant in an isolated system
- Which of the following best defines an isolated system?
- A) A system with external forces acting on it
- B) A system with no mass
- C) A system with bodies interacting within certain borders without external forces
- D) A system with infinite momentum
- Answer: C) A system with bodies interacting within certain borders without external forces
- What factors does the momentum of a system depend on?
- A) Mass only
- B) Velocity only
- C) Both mass and velocity
- D) Neither mass nor velocity
- Answer: C) Both mass and velocity
- In the equation for the law of conservation of momentum, what does “m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2” represent?
- A) Initial momentum before collision = Final momentum after collision
- B) Final momentum before collision = Initial momentum after collision
- C) Total momentum before collision = Total momentum after collision
- D) Momentum is not conserved in a collision
- Answer: A) Initial momentum before collision = Final momentum after collision
- Which principle states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction?
- A) Newton’s First Law
- B) Newton’s Second Law
- C) Newton’s Third Law
- D) Newton’s Law of Gravitation
- Answer: C) Newton’s Third Law
- What occurs to the momentum of an isolated system if no external force acts upon it?
- A) It decreases
- B) It increases
- C) It remains constant
- D) It becomes infinite
- Answer: C) It remains constant
- What is the momentum of an isolated system if no unbalanced force acts upon it?
- A) Increasing
- B) Decreasing
- C) Consistent
- D) Fluctuating
- Answer: C) Consistent
- In a collision, what does the law of conservation of momentum indicate about the total momentum?
- A) It decreases
- B) It increases
- C) It remains the same
- D) It becomes zero
- Answer: C) It remains the same
- Which scenario illustrates the conservation of momentum?
- A) A moving object stopping suddenly
- B) A rocket accelerating in space
- C) A ball rolling downhill
- D) A car slowing down at a traffic light
- Answer: B) A rocket accelerating in space
- What is the total momentum of an isolated system before and after a collision, according to the law of conservation of momentum?
- A) It remains constant
- B) It increases
- C) It decreases
- D) It becomes zero
- Answer: A) It remains constant
- How does the law of conservation of momentum apply to a gun firing a bullet?
- A) The gun absorbs all momentum
- B) The bullet recoils with equal momentum to the gun
- C) The gun recoils with equal momentum to the bullet
- D) Momentum is not conserved in this scenario
- Answer: C) The gun recoils with equal momentum to the bullet
- Which example demonstrates the law of conservation of momentum?
- A) A skateboarder slowing down on a ramp
- B) A bird flying in the sky
- C) A cannon shooting a cannonball
- D) A boat drifting in water
- Answer: C) A cannon shooting a cannonball
- How do rockets and jet engines utilize the law of conservation of momentum?
- A) By conserving kinetic energy
- B) By releasing hot gases with large momentum
- C) By reducing momentum to increase speed
- D) By violating the law of conservation of momentum
- Answer: B) By releasing hot gases with large momentum
- What does the law of conservation of momentum say about the overall momentum of a system?
- A) It fluctuates
- B) It decreases over time
- C) It remains constant
- D) It increases indefinitely
- Answer: C) It remains constant
- In a collision between two objects, if one object gains momentum, what happens to the other?
- A) It loses momentum
- B) It gains momentum
- C) Its momentum remains unchanged
- D) Its mass increases
- Answer: A) It loses momentum
- Which scenario does not obey the law of conservation of momentum?
- A) Two ice skaters pushing each other on ice
- B) A baseball being hit by a bat
- C) A skateboarder performing tricks on a half-pipe
- D) A car colliding with a stationary object
- Answer: D) A car colliding with a stationary object
- How does the law of conservation of momentum apply to everyday phenomena?
- A) It explains why objects float
- B) It describes how sound travels through air
- C) It helps understand the motion of objects in collisions
- D) It determines the color of objects
- Answer: C) It helps understand the motion of objects in collisions
- What is the significance of an isolated system in the context of momentum conservation?
- A) It ensures external forces do not affect momentum
- B) It accelerates momentum
- C) It reduces momentum
- D) It creates momentum
- Answer: A) It ensures external forces do not affect momentum
FAQs Related to the Law of Conservation of Momentum
- What is the Law of Conservation of Momentum?
- The Law of Conservation of Momentum states that the momentum of an isolated system remains constant if no external forces act upon it.
- How is momentum defined in the context of the law?
- Momentum is the product of an object’s mass and its velocity. In other words, momentum = mass × velocity.
- What constitutes an isolated system?
- An isolated system is a group of bodies that interact with each other, but no external forces act upon them. This means that the system is closed off from any external influence.
- Why is momentum conservation significant in physics?
- Momentum conservation is significant because it helps us understand and predict the motion of objects, especially in collisions or interactions between multiple bodies.
- Can you explain the mathematical expression of the Law of Conservation of Momentum?
- The mathematical expression states that the total initial momentum of a system before a collision equals the total final momentum of the system after the collision. Mathematically, it’s represented as Σ(initial momenta) = Σ(final momenta).
- What are some real-world examples of the Law of Conservation of Momentum?
- Examples include the recoil of a gun when a bullet is fired, the propulsion of rockets and jet engines, and collisions between various objects like billiard balls or vehicles.
- How does the Law of Conservation of Momentum apply to the example of a gun firing a bullet?
- When a gun fires a bullet, the bullet gains momentum in one direction, causing the gun to recoil in the opposite direction, conserving the total momentum of the system.
- Do rockets and jet engines follow the Law of Conservation of Momentum?
- Yes, rockets and jet engines operate on the principle of conservation of momentum. They expel hot gases with high momentum in one direction, causing the vehicle to move in the opposite direction.
- Are there any exceptions to the Law of Conservation of Momentum?
- In everyday scenarios, the law holds true. However, at the quantum level or in extreme conditions such as relativistic speeds or near black holes, there might be deviations from classical momentum conservation.
- How does the Law of Conservation of Momentum relate to Newton’s Third Law of Motion?
- Newton’s Third Law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This principle is closely related to momentum conservation, particularly in situations involving collisions or interactions between objects.
