What is Erythroblastosis fetalis?
Erythroblastosis fetalis is a serious medical condition that most frequently results from an incompatibility between certain blood types of a woman who is pregnant and the fetus. The condition involves an element of blood called the Rh factor. Rh factor is an inherited protein, present on the surface of the red cells.
Not everybody has this protein. If a person has the protein, they are Rh-positive. Those who do not have the Rh protein are Rh-negative. If a woman is Rh-negative and the fetus is Rh-positive, it can lead to Rh incompatibility and potential issues in the pregnancy.
Maternal-foetal Rh incompatibility
Maternal-fetal incompatibility results when an Rh- female, married to an Rh+ man conceives a child who is Rh+. If the man’s genotype is DD, all of their offspring (Dd) will be Rh+. If the man’s genotype is Dd, half of their offspring with Dd genotype will be Rh+.
If RBC of Rh+ fetus crosses the placental barrier and enters into Rh- mother’s bloodstream, the mother’s immune system reacts to the foetal Rh antigen stimulus by producing a great deal of anti – Rh antibodies. When the mother’s anti – Rh antibodies leak through the placenta into the blood circulation of foetus, they start hemolysis (break down/ rupturing) of RBC of the fetus. As this damage continues, the foetus ends up being anemic. The anemic foetus starts to release lots of -immature erythroblasts into his bloodstream.

That is why this hemolytic illness of the newborn is called erythroblastosis fetalis. This anemia may result in abortion or stillbirth. Even if the pregnancy continues, the liver and spleen of the foetus swell as they rapidly produce RBC. The breakdown product of RBC called bilirubin also accumulates in the foetus.
Bilirubin harms his brain cells and turns his skin and whites of the eye yellow. This condition is called jaundice. So, the child if born alive, suffer from severe hemolytic anemia and jaundice. Such an infant’s blood must be immediately changed by Rh” blood without anti – Rh antibodies.
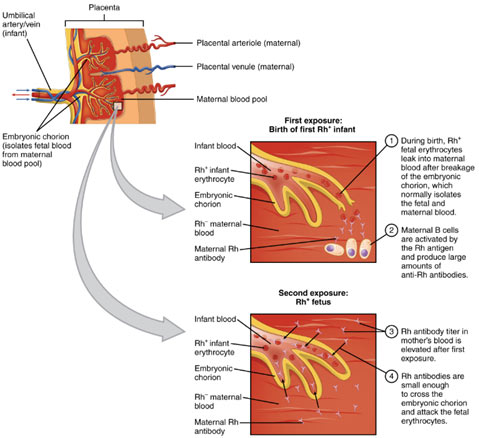
The first Rh incompatible pregnancy may not face many problems if extremely few fetal antigens cross the placenta into maternal circulation and the quantity of maternal antibody production is not very high. But when the placenta separates at birth, a large number of fetal cells get into the mother’s bloodstream and promote the production of a big quantity of anti – Rh antibodies by the mother. These anti – Rh antibodies persist in the mother’s blood for a long time and are a relentless risk for the next Rh+ fetus.
When Erythroblastosis fetalis can happen?
Erythroblastosis fetalis can happen when various Rh factor blood types mix during pregnancy. Problems can emerge even if small amounts of Rh-positive and Rh-negative blood mix. Although it is rare for blood in between the female and the fetus to blend during pregnancy, it might occur as a result of:
- the placenta detaching from the wall of the uterus wall during delivery
- bleeding during pregnancy
- manual rotation of a breech baby
- an ectopic pregnancy
- a miscarriage
- a fall, blunt injury, or invasive prenatal testing
- prenatal tests, such as an amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
How it can be treated?
If a baby experiences erythroblastosis fetalis in the womb, they may be given intrauterine blood transfusions to minimize anemia. When the child’s lungs and heart mature enough for delivery, a physician might advise delivering the infant early. After a baby is born, additional blood transfusions might be required.
Providing infant fluids intravenously can enhance low blood pressure. The baby may also require momentary breathing support from a ventilator or mechanical breathing machine.
How it can be prevented?

Rh sensitization of Rh- mother is prevented by a simple therapy. She is given an injection of Rh antiserum during early pregnancy and immediately after birth. The Rh – antibodies in the Rh antiserum will destroy Rh+ RBC of the fetus prior to they promote the production of maternal anti – Rh antibodies. The injected antiserum vanishes before the next pregnancy.
Sometimes a mild ABO incompatibility prevents the child from a more severe Rh incompatibility. If O’ mother develops A+ or B+ baby, any fetal A or B type RBCgoing into the mother’s blood are rapidly damaged by her anti-A or anti-B antibodies, prior to she can form anti – Rh antibodies.
Summary
The incompatibility between certain types of maternal and fetal blood groups results in a disorder of hemolytic anemia; called erythroblastosis fetalis. It happens when Rh- female conceives a Rh+ child.
When red blood cells of fetus cross the placenta and enter into mother’s bloodstream. The mother’s defense system reacts to it and produces anti-Rh- antibodies. When these antibodies enter the fetus blood, they start rupturing blood.
The bilirubin from breaks down of red blood cells accumulate in fetus and cause damage to brain and turns the skin to yellow color. This condition is jaundice.
