What is the Doppler Effect?
When the source and observer are moving relative to each other, the frequency observed by the observer (fa) is different from the actual frequency produced by the source (f). This is the Doppler effect. Here, when the source of waves is moving toward the observer, they will have an upward frequency shift. As for the observers from whom the source is declining, there will be a downshift in frequency.
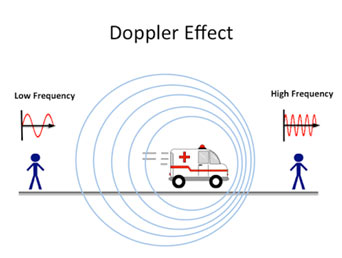
Nevertheless, it must be kept in mind that the result does not happen as a result of the actual change in the frequency of the wave source. The Doppler effect can be observed in both sound waves and light waves.
The primary reason that we experience this impact is that as the wave source moves toward the observer, each new wave crest that is formed from the source is given off from a place that is closer to the observer. Therefore, as the source moves closer and closer the waves will now take less time to reach the observer, or the time between the arrivals of new-age crests is decreased.
This further causes an increase in frequency. Likewise, when the source of waves is going away, the waves are given off from a farther area thus increasing the arrival time in between each new wave. This results in a decrease in frequency.
Nevertheless, from what we have learned above, we can sum up that the Doppler effect might arise from aspects such as the motion of the observer, the movement of the source, or the motion of the medium. This is mainly real for sound waves.
Whereas, for waves that can travel in any medium, such as light, we require to consider just the relative difference in speed between the source and the observer.
Doppler Effect Formula
The sound heard by the listener changes if the source of that noise and the listener are moving relative to each other. This is what the Doppler Effect is. When the listener and the source move close, the frequency which the listener heard is higher than the noise which the source produces.
Similarly, when the listener and the source move far from one another, the frequency which the listener hears is lower than the frequency of the sound from the source. The unit of sound frequency is Hertz (Hz). Over here, one Hertz is a cycle per second (1 Hz = 1 s-1 = 1 cycle/s).
Hence, the equation comes as:
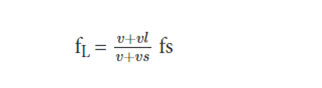
Where
- FL refers to the frequency of sound which the listener hears (Hz, or 1/s)
- v is the velocity of sound in the medium (m/s)
- vL describes the velocity of the listener (m/s)
- vs is the velocity of the source of the noise (m/s)
- fs refers to the frequency of sound which the source emits (Hz, or 1/s)
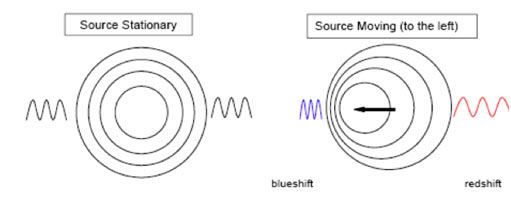
Types of Doppler Shift
There are two types of Doppler shifts:
- Red-Shift or a shift of frequency to a lower wavelength (away from the observer).
- Blue-Shift or a shift of frequency to a higher wavelength (towards the observer).
Applications of Doppler Effect
(i) To determine the speed of an automobile
An electromagnetic wave is produced by a source connected to a police car. The wave is shown by a moving vehicle, which functions as a moving source. There is a shift in the frequency of the shown wave. From the frequency shift using beats, the speeding cars are trapped by the cops.
(ii) Tracking a satellite
The frequency of radio waves produced by a satellite reduces as the satellite passes away from the Earth. The frequency received by the Earth station, combined with a constant frequency generated in the station offers the beat frequency. Utilizing this, a satellite is tracked.
(iii) RADAR (RADIO DETECTION AND RANGING)
A RADAR sends high-frequency radio waves toward an aeroplane. The reflected waves are identified by the receiver of the radar station. The difference in frequency is used to figure out the speed of an aeroplane.
(iv) SONAR (SOUND NAVIGATION AND RANGING)
Sound waves generated from a ship fitted with SONAR are transferred in the water towards an approaching submarine. The frequency of the reflected waves is determined and hence the speed of the submarine is determined.
MCQs:
- What is the Doppler Effect primarily concerned with?
- A) Changes in the frequency of waves
- B) Changes in the speed of light
- C) Changes in the wavelength of sound waves
- D) Changes in the amplitude of waves
- Answer: A) Changes in the frequency of waves
- Which scenario results in an upward shift in frequency according to the Doppler Effect?
- A) Source moving away from the observer
- B) Source and observer moving closer to each other
- C) Observer moving towards the source
- D) Source and observer at rest relative to each other
- Answer: B) Source and observer moving closer to each other
- The Doppler Effect can be observed in which types of waves?
- A) Only sound waves
- B) Only light waves
- C) Both sound and light waves
- D) Neither sound nor light waves
- Answer: C) Both sound and light waves
- What factor primarily contributes to the change in frequency observed in the Doppler Effect?
- A) Change in the wavelength of the wave
- B) Motion of the observer
- C) Change in the amplitude of the wave
- D) Speed of the medium through which the wave travels
- Answer: B) Motion of the observer
- What does FL represent in the Doppler Effect equation?
- A) Frequency of the sound emitted by the source
- B) Frequency of the sound heard by the listener
- C) Speed of the sound in the medium
- D) Speed of the listener
- Answer: B) Frequency of the sound heard by the listener
- What is the unit of sound frequency?
- A) Watt
- B) Joule
- C) Hertz
- D) Newton
- Answer: C) Hertz
- Which type of Doppler shift indicates a shift to a lower frequency?
- A) Red-Shift
- B) Blue-Shift
- C) Green-Shift
- D) Yellow-Shift
- Answer: A) Red-Shift
- In the Doppler Effect, what does the blue-shift signify?
- A) Movement of the observer away from the source
- B) Movement of the observer towards the source
- C) Movement of the source away from the observer
- D) No motion between the observer and the source
- Answer: B) Movement of the observer towards the source
- Which application of the Doppler Effect is used to determine the speed of automobiles?
- A) Tracking a satellite
- B) Radar
- C) Sonar
- D) Monitoring police speed guns
- Answer: D) Monitoring police speed guns
- How is the speed of an approaching satellite tracked using the Doppler Effect?
- A) By monitoring the frequency shift of radio waves
- B) By analyzing the amplitude of radio waves
- C) By measuring the speed of light
- D) By detecting changes in the wavelength of sound waves
- Answer: A) By monitoring the frequency shift of radio waves
- What is RADAR primarily used for in relation to the Doppler Effect?
- A) Tracking submarines
- B) Monitoring weather patterns
- C) Determining the speed of airplanes
- D) Detecting the presence of police speed guns
- Answer: C) Determining the speed of airplanes
- How does SONAR utilize the Doppler Effect?
- A) To track the speed of submarines
- B) To measure the depth of oceans
- C) To monitor the movement of satellites
- D) To analyze the frequency of light waves
- Answer: A) To track the speed of submarines
- What phenomenon occurs when a source of waves is moving towards an observer in the Doppler Effect?
- A) Upward shift in frequency
- B) Downward shift in frequency
- C) No change in frequency
- D) Increase in wavelength
- Answer: A) Upward shift in frequency
- What aspect of a moving source contributes to the Doppler Effect?
- A) Change in amplitude
- B) Change in wavelength
- C) Change in speed
- D) Change in distance from the observer
- Answer: C) Change in speed
- Which type of Doppler shift is associated with a shift to a higher frequency?
- A) Red-Shift
- B) Blue-Shift
- C) Green-Shift
- D) Yellow-Shift
- Answer: B) Blue-Shift
- How is the speed of an airplane determined using RADAR?
- A) By analyzing changes in the amplitude of reflected waves
- B) By measuring the speed of light
- C) By tracking changes in the frequency of radio waves
- D) By detecting changes in the color of light waves
- Answer: C) By tracking changes in the frequency of radio waves
- Which application of the Doppler Effect is primarily used for tracking underwater objects?
- A) Radar
- B) Monitoring police speed guns
- C) Sonar
- D) Tracking satellites
- Answer: C) Sonar
- What is the primary factor leading to a decrease in frequency observed in the Doppler Effect?
- A) Movement of the observer towards the source
- B) Movement of the source away from the observer
- C) No motion between the observer and the source
- D) Decrease in the speed of the medium
- Answer: B) Movement of the source away from the observer
- Which type of waves exhibit the Doppler Effect?
- A) Only mechanical waves
- B) Only electromagnetic waves
- C) Both mechanical and electromagnetic waves
- D) Neither mechanical nor electromagnetic waves
- Answer: C) Both mechanical and electromagnetic waves
FAQs Related to Doppler Effect:
- What is the Doppler Effect and how does it occur?
- The Doppler Effect refers to the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It occurs when there is relative motion between the source of the wave and the observer.
- Can the Doppler Effect be observed in both sound waves and light waves?
- Yes, the Doppler Effect can be observed in both sound waves and light waves.
- What factors contribute to the Doppler Effect in sound waves?
- The Doppler Effect in sound waves can be influenced by the motion of the observer, the movement of the source, or the motion of the medium through which the sound waves propagate.
- What are the types of Doppler Shift?
- There are two types of Doppler shifts: Red-Shift, which is a shift of frequency to a lower wavelength (away from the observer), and Blue-Shift, which is a shift of frequency to a higher wavelength (towards the observer).
- What are some applications of the Doppler Effect?
- The Doppler Effect has various applications, including determining the speed of automobiles, tracking satellites, radar systems for determining the speed of airplanes, and sonar systems for tracking underwater objects such as submarines.
- How is the Doppler Effect utilized in determining the speed of automobiles?
- In monitoring speed, a police car emits electromagnetic waves, which are reflected off moving vehicles, resulting in a frequency shift. This shift is used to determine the speed of the vehicles.
- How is the Doppler Effect used in tracking satellites?
- The frequency of radio waves emitted by a satellite decreases as it moves away from the Earth. By measuring this frequency shift, satellites can be tracked.
- What is the principle behind RADAR systems in relation to the Doppler Effect?
- RADAR systems send high-frequency radio waves towards objects such as airplanes. The frequency shift in the reflected waves is analyzed to determine the speed of the objects.
- How does SONAR utilize the Doppler Effect in tracking underwater objects?
- SONAR systems emit sound waves towards objects such as submarines. The frequency shift in the reflected waves is analyzed to determine the speed and position of the objects underwater.
Summary:
The Doppler Effect is a phenomenon where the observed frequency of a wave differs from the actual frequency due to relative motion between the source and observer. This effect is observed in both sound waves and light waves.
As the wave source moves towards the observer, there is an upward shift in frequency, while movement away from the observer causes a downward shift. This change in frequency is not due to an actual change in the source’s frequency but is a result of relative motion.
The Doppler Effect can be described using a formula, taking into account the velocity of sound, the velocity of the observer, and the velocity of the source. There are two types of Doppler shifts: Red-Shift, which indicates a shift to a lower frequency, and Blue-Shift, which indicates a shift to a higher frequency.
The Doppler Effect finds applications in various fields, including determining the speed of automobiles, tracking satellites, radar systems for airplanes, and sonar systems for submarines. These applications utilize the frequency shift of waves to measure the speed and position of moving objects.
