Distribution of life on Earth
According to some biologists, the distribution of life on Earth has three aspects, two of which deal with the distribution of life in space and one in time. The two stages of spatial distribution are very closely related to each other however are typically studied separately as Bathymetric and Geographic distribution.
The distribution of life with respect to time, present and past, is called Geologic or Durational distribution.
Bathymetric distribution
Bathymetric distribution deals with the vertical distribution of organisms in space, i.e., from the high Himalayan-Alpine peaks to the abyssal depth of the sea. Bathymetric distribution concerns itself with the vertical range of organisms in space, and indicates much more than simple altitude, for in passing from the highest alpine peak to the abyssal depths of the sea one would find a series of contrasting conditions which of necessity exceptionally affect the organism.
From a bathymetric viewpoint, three major realms may be acknowledged as
Limnobiotic Distribution
It deals with the vertical distribution of animals in freshwater sources.
Holobiotic Distribution
The vertical distribution of animals in the sea or marine environments.
Geobiotic Distribution
It describes the distribution of life on land. This extends from the highest tidemark along the shores of all continents to the summit of the greatest mountains. The progressive changes in temperature level, light, rains, and other climatic elements from the equator towards poles and from lowlands to the mountain peaks control the distribution of specific significant plant life types and these, in turn, are accompanied by particular sets of animal species.

The continental life zones are formed by the approximately latitudinal plans of specific the primary biotic formations or Biomes. Each biome has its unique set of conditions and each supports a particular kind of animal and flora. Some of the important terrestrial biomes recognized by ecologists are the tundra biome, alpine biome, forest biome, grassland biome, desert biome.
Geographical or Horizontal Distribution
The distribution of animals on land and fresh water in different continents and on different islands is called geographical or horizontal distribution.
Zoogeography is the study of the distribution of animals and plants on our planet, which occur in various regions of the world in a unique pattern. The distribution of some animal species is so peculiar that it is challenging to explain their occurrence in a particular region.
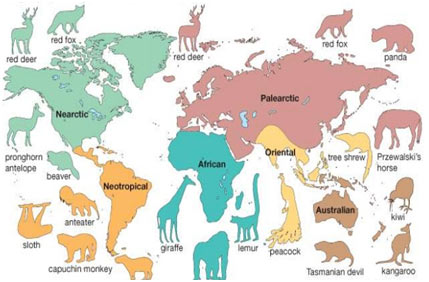
Zoogeography efforts to understand the complexities along with the simpleness in the distribution of animals in the light of evolutionary and environmental impacts.
Phytogeography deals with the distribution of plants only, more particularly the vascular plants i.e., the plants that have vessels or vascular bundles for transport of water and food.
Geological distribution
The distribution of animals in the past of Earth’s history is called the distribution in time. This can be studied by fossil evidence only. The description of this type of distribution can be made on the Geological time scale.

The geological distribution is extremely important for understanding the process of evolution. The branch of geology which concerns the study of ancient life from fossils is called paleontology.
1. What is the distribution of life on Earth?
- The distribution of life on Earth involves three main aspects: two related to spatial distribution and one to temporal distribution.
2. What are the spatial aspects of the distribution of life?
- Spatial distribution includes Bathymetric and Geographical distributions. Bathymetric distribution deals with vertical distribution, while Geographical distribution refers to horizontal distribution.
3. What is Bathymetric distribution?
- Bathymetric distribution concerns the vertical distribution of organisms in space, from high altitudes to abyssal depths in the sea. It includes Limnobiotic, Holobiotic, and Geobiotic distributions.
4. What is Limnobiotic Distribution?
- Limnobiotic distribution focuses on the vertical distribution of animals in freshwater sources.
5. What is Holobiotic Distribution?
- Holobiotic distribution pertains to the vertical distribution of animals in marine environments.
6. What is Geobiotic Distribution?
- Geobiotic distribution describes the distribution of life on land, from shorelines to mountain peaks, influenced by various climatic factors.
7. What are some examples of terrestrial biomes?
- Important terrestrial biomes include the tundra, alpine, forest, grassland, and desert biomes.
8. What is Geographical or Horizontal Distribution?
- Geographical or Horizontal Distribution refers to the distribution of animals on land and freshwater across continents and islands.
9. What is Zoogeography?
- Zoogeography is the study of the distribution patterns of animals on Earth, influenced by evolutionary and environmental factors.
10. What does Phytogeography focus on?
- Phytogeography focuses on the distribution of plants, particularly vascular plants with specialized transport systems.
11. What does Geological Distribution refer to?
- Geological Distribution refers to the distribution of animals throughout Earth’s history, studied through fossil evidence on the Geological time scale.
12. Why is Geological Distribution important?
- Geological Distribution aids in understanding the process of evolution and is crucial in the field of paleontology, the study of ancient life through fossils.
Summary:
The distribution of life on Earth encompasses spatial and temporal dimensions. Spatially, it is classified into Bathymetric and Geographical distributions, while temporally it involves Geological distribution.
Bathymetric distribution examines the vertical distribution of organisms, distinguishing between Limnobiotic (freshwater), Holobiotic (marine), and Geobiotic (terrestrial) realms. Geobiotic distribution spans from shorelines to mountain peaks, characterized by varying climatic conditions and the formation of distinct biomes.
Geographical distribution focuses on the spread of life across continents and islands, studied through Zoogeography and Phytogeography, which explore animal and plant distribution patterns. Geological distribution examines the historical distribution of life through fossil evidence, essential for understanding evolution and studied within the field of paleontology.

