Diseases of the Endocrine System
Endocrine disorders are diseases related to the endocrine glands of the body.
- The endocrine system produces hormones, which are chemical signals sent, or produced, through the bloodstream.
- Hormones assist the body in managing and regulating processes, such as appetite, breathing, growth, fluid balance, feminization and virilization, and weight control.
- The endocrine system includes several glands, consisting of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus in the brain, adrenal glands in the kidneys, and thyroid in the neck, along with the pancreas, ovaries, and testes.
- The stomach, liver, and intestinal tracts also produce hormones related to digestion. Most typical endocrine disorders are related to improper functioning of the pancreas and the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands.
There are various types of endocrine disorders. Some of them are the following:
- 1) 1.Gigantism (acromegaly)
- 2) 2. Dwarfism
- 3) 3. Addison’s disease
- 4) 4. Hyperthyroidism
- 5) 5. Graves’ disease
- 6) 6. Cretinism
- 7) 7. Goiter
- 8) 8. Hypothyroidism/ myxoedema
- 9) 9. Diabetes insipidus
- 10) 10. Diabetes Mellitus
- 11) Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) with Answers: Diseases of Endocrine System
- 12) FAQs – Diseases of Endocrine System in Human Beings
- 13) Summary: Diseases of Endocrine System in Human Beings
- 14) You may also like to learn:
1.Gigantism (acromegaly)
Acromegaly is a disorder in which the pituitary gland overproduces growth hormone. This results in signs of overgrowth, especially of the hands and feet. Symptoms of acromegaly include: Abnormally big lips, nose or tongue, abnormally large or swollen hands or feet, changed facial bone structure, overgrowth of bone and cartilage and thickening of the skin, etc.
2. Dwarfism
Due to the under-secretion of somatotrophin hormone, a child can stop growing in height. This led to dwarfism. In addition to short stature, dwarfism has many other symptoms that can vary depending on the type it is.
3. Addison’s disease
Addison’s disease is characterized by decreased production of cortisol and aldosterone due to adrenal gland damage. Common signs of Addison’s disease include:
- Tiredness
- Headache
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar level)
- Anorexia nervosa
- Inexplicable weight reduction
- Weakness (loss of strength)
4. Hyperthyroidism
The thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, resulting in weight loss, rapid heart rate, sweating, and nervousness. The most common cause for an overactive thyroid is an autoimmune disorder called Graves disease.
5. Graves’ disease
Excess thyroxine produces a condition called Graves’ disease, with exophthalmic goiter and an increase in the basal metabolic rate. This can lead to cardiac failure if remains for a long time. The cause of Graves’ disease is the production of an abnormal body protein that continually stimulates the thyroid to extreme secretion.
6. Cretinism
If congenitally deficient, the lack of thyroxine causes cretinism, where the individual fails to develop normally. They are small, have coarse scanty hair, thick yellow-colored scaly skin, and are psychologically retarded. They also fail to develop sexually.
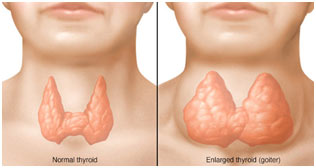
7. Goiter
A goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland situated at the base of your neck simply below your Adam’s apple. Although goiters are usually pain-free, a large goiter can trigger a cough and make it challenging for you to swallow or breathe. It is perhaps due to iodine shortage in the diet plan, produces swelling of the neck (goiter) and may cause deposition of excess fat as a result of which weight is increased.
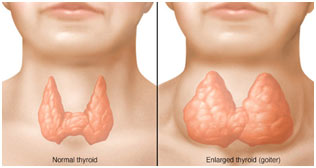
8. Hypothyroidism/ myxoedema
When the thyroid gland produces too little thyroid hormone, fatigue, constipation, dry skin, and depression can occur. In kids, hypothyroidism can cause slowed growth. It is likewise identified by the puffiness of hands and skin.
9. Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus is an uncommon condition that triggers an imbalance of fluids in the body. This imbalance makes you extremely thirsty even if you have had something to consume. It also leads you to produce large quantities of urine. This is due to the lack of a hormone called anti-diuretic hormone (ADH), or vasopressin. Signs and symptoms of diabetes insipidus consist of:
- Severe thirst
- Making large quantities of diluted urine
- The frequent requirement to get up to urinate throughout the night
10. Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus frequently referred to as diabetes, is a metabolic illness that triggers high blood glucose levels. The hormone insulin moves sugar from the blood into your cells to be kept or used for energy. With diabetes, your body either doesn’t make sufficient insulin or can’t efficiently use the insulin it does make. There are a few kinds of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. The body’s immune system attacks and destroys cells in the pancreas, where insulin is made. It’s unclear what triggers this attack. About 10 percent of individuals with diabetes have this type.
- Type 2 diabetes happens when your body ends up being resistant to insulin, and sugar develops in your blood.
- Prediabetes happens when your blood glucose is higher than normal, but it’s not high enough for a medical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes is high blood sugar level during pregnancy. Insulin-blocking hormonal agents produced by the placenta cause this kind of diabetes.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) with Answers: Diseases of Endocrine System
- What is acromegaly?
- a) Overproduction of insulin
- b) Overproduction of growth hormone
- c) Underproduction of cortisol
- d) Underproduction of thyroxine
- Answer: b
- Which hormone deficiency leads to dwarfism?
- a) Cortisol
- b) Somatotrophin
- c) Thyroxine
- d) Insulin
- Answer: b
- What are the common symptoms of Addison’s disease?
- a) Rapid heart rate and weight loss
- b) Tiredness and headache
- c) Excessive thirst and diluted urine
- d) Coarse hair and skin thickening
- Answer: b
- Hyperthyroidism is characterized by:
- a) Overproduction of insulin
- b) Overproduction of cortisol
- c) Overproduction of thyroid hormone
- d) Underproduction of growth hormone
- Answer: c
- What causes Graves’ disease?
- a) Iodine deficiency
- b) Autoimmune disorder
- c) Overproduction of cortisol
- d) Underproduction of insulin
- Answer: b
- What does congenital deficiency of thyroxine lead to?
- a) Gigantism
- b) Diabetes insipidus
- c) Cretinism
- d) Goiter
- Answer: c
- What is the abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland called?
- a) Gigantism
- b) Goiter
- c) Cretinism
- d) Dwarfism
- Answer: b
- Hypothyroidism is characterized by:
- a) Overproduction of thyroid hormone
- b) Underproduction of insulin
- c) Underproduction of cortisol
- d) Underproduction of thyroid hormone
- Answer: d
- Diabetes insipidus is due to the lack of which hormone?
- a) Insulin
- b) Cortisol
- c) Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
- d) Thyroxine
- Answer: c
- What does diabetes mellitus cause?
- a) Low blood sugar levels
- b) High blood sugar levels
- c) Low blood pressure
- d) Elevated cortisol levels
- Answer: b
- What is the cause of Type 1 diabetes?
- a) Insulin resistance
- b) Autoimmune attack on pancreas cells
- c) Overproduction of insulin
- d) Lack of growth hormone
- Answer: b
- What happens in Type 2 diabetes?
- a) Body becomes resistant to insulin
- b) Autoimmune attack on pancreas cells
- c) Overproduction of growth hormone
- d) Lack of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
- Answer: a
FAQs – Diseases of Endocrine System in Human Beings
1. What are endocrine disorders?
- Endocrine disorders are diseases related to the improper functioning of the endocrine glands, leading to hormonal imbalances in the body.
2. Which glands are part of the endocrine system?
- The endocrine system includes glands such as the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, adrenal glands, thyroid, pancreas, ovaries, and testes.
3. What is acromegaly, and what are its symptoms?
- Acromegaly is a disorder where the pituitary gland overproduces growth hormone, leading to overgrowth, especially of the hands and feet. Symptoms include abnormally large lips, nose, or tongue, swollen hands or feet, changed facial bone structure, and thickening of the skin.
4. How does dwarfism occur?
- Dwarfism occurs due to the undersecretion of somatotrophin hormone, leading to a child stopping growth in height.
5. What are the common signs of Addison’s disease?
- Common signs of Addison’s disease include tiredness, headache, hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), anorexia nervosa, unexplained weight loss, and weakness.
6. What is the cause of hyperthyroidism, and what are its effects?
- Hyperthyroidism is caused by the overproduction of thyroid hormone, resulting in weight loss, rapid heart rate, sweating, and nervousness. Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder, is a common cause.
7. What characterizes Graves’ disease?
- Graves’ disease is characterized by excess thyroxine production, resulting in exophthalmic goiter and an increased basal metabolic rate. Prolonged cases can lead to cardiac failure.
8. What is cretinism, and how does it manifest?
- Cretinism occurs due to congenital thyroxine deficiency, leading to abnormal development. Symptoms include small stature, coarse scanty hair, thick yellow-colored scaly skin, and mental retardation.
9. What is a goiter, and what can cause it?
- A goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland. Iodine deficiency in the diet can cause a goiter, leading to neck swelling and, in severe cases, difficulty swallowing or breathing.
10. How is hypothyroidism/myxoedema characterized? – Hypothyroidism/myxoedema is characterized by the underproduction of thyroid hormone, leading to fatigue, constipation, dry skin, and depression. In children, it can cause slowed growth and is marked by puffiness of hands and skin.
11. What is diabetes insipidus, and what are its symptoms? – Diabetes insipidus is a rare condition causing fluid imbalance, extreme thirst, large amounts of diluted urine, and frequent urination during the night. It results from a lack of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH).
12. What is diabetes mellitus, and how does it affect the body? – Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a metabolic disease causing high blood sugar levels. It occurs when the body doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin it produces. Diabetes has different types, including Type 1, Type 2, prediabetes, and gestational diabetes.
Summary: Diseases of Endocrine System in Human Beings
The tutorial on diseases of the endocrine system explores various disorders arising from the malfunctioning of endocrine glands, which produce hormones regulating critical bodily processes. The endocrine system encompasses glands such as the pituitary, hypothalamus, adrenal, thyroid, pancreas, ovaries, and testes.
Notable disorders discussed include:
- Gigantism (Acromegaly): Caused by the pituitary gland overproducing growth hormone, leading to abnormal overgrowth, especially in hands and feet.
- Dwarfism: Results from the undersecretion of somatotrophin hormone, causing a child to cease growing in height.
- Addison’s Disease: Characterized by reduced cortisol and aldosterone production due to adrenal gland damage, with symptoms including fatigue, headache, and hypoglycemia.
- Hyperthyroidism (Graves’ Disease): Excessive thyroid hormone production leading to weight loss, rapid heart rate, and sweating, often associated with Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder.
- Cretinism: Congenital thyroxine deficiency causing abnormal development, characterized by small stature, coarse hair, and mental retardation.
- Goiter: Abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, potentially caused by iodine deficiency, resulting in neck swelling.
- Hypothyroidism/Myxoedema: Insufficient thyroid hormone production leading to fatigue, constipation, and depression, marked by puffiness of hands and skin.
- Diabetes Insipidus: Rare condition causing fluid imbalance, extreme thirst, and excessive urine production due to the lack of anti-diuretic hormone.
- Diabetes Mellitus: A metabolic disease, with types including Type 1 (autoimmune), Type 2 (insulin resistance), Prediabetes, and Gestational Diabetes during pregnancy.
Understanding these disorders is crucial for recognizing symptoms, diagnosis, and appropriate medical interventions, emphasizing the significance of a well-functioning endocrine system for overall health.