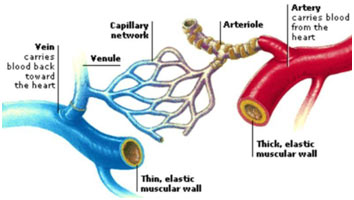
Understanding the circulatory system involves exploring the intricate network of blood vessels that play a pivotal role in the transportation of blood throughout the body.
Arteries, veins, and capillaries, the primary components of this vascular system, exhibit distinct characteristics that contribute to their specialized functions.
In the table below, we explained the differences between arteries, veins, and capillaries, shedding light on their anatomical features, blood flow dynamics, and physiological roles.
Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries Differences
| Sr.no. | Arteries | Veins | Capillaries |
| 1. | These are responsible for the transportation of blood from the heart to all parts of the body. | These vessels collect blood through capillaries and transport it towards the heart. | These vessels connect arteries and veins. |
| 2. | All arteries carry oxygenated blood except pulmonary arteries which carry deoxygenated blood. | All veins carry deoxygenated blood except pulmonary veins which carry oxygenated blood. | These carry mixed oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. |
| 3. | Arteries have no valves in them except at the base of the pulmonary trunk and aorta. | Valves are present in veins. These valves prevent the backflow of blood. | There are no valves in them. |
| 4. | Arteries have high blood pressure. | Veins have low blood pressure. | There is falling pressure in them. |
| 5. | In arteries, waves of blood pressure or pulse due to heartbeat can be detected. | There is no pulse. | There is no pulse. |
| 6. | Blood flows rapidly between 400-500mm per second in the aorta and decreasing in arteries and arterioles. | The rate of blood flow increases from smaller to larger veins. | Blood flow is slowest which is less than 1mm per second. |
| 7. | Arteries have a smaller bore and thick walls. | Veins have a larger bore and thin walls. | Capillaries have a larger bore and the wall is of one cell in thickness. |
| 8. | There are thick muscle layers and elastic fibers present. The elasticity helps to change the pulsating flow of blood. | There are thin muscle layer and less elastic fibers present in veins. So, they are less elastic. | No muscles or elastic fibers are present. |
| 9. | There is no exchange of materials. | There is no exchange of materials. | These are responsible for the exchange of gases and nutrients. |
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) – Difference Between Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries:
- What is the primary function of arteries?
- A) Collect blood from capillaries
- B) Transport blood towards the heart
- C) Connect arteries and veins
- D) Facilitate exchange of gases
Answer: B) Transport blood towards the heart
- Which type of blood do pulmonary veins carry?
- A) Oxygenated
- B) Deoxygenated
- C) Mixed oxygenated and deoxygenated
- D) Nutrient-rich
Answer: A) Oxygenated
- Where are valves typically found in veins?
- A) At the base of the pulmonary trunk
- B) Throughout the vessel
- C) In the aorta
- D) At the junction with capillaries
Answer: B) Throughout the vessel
- What characterizes the blood pressure in veins?
- A) High blood pressure
- B) Low blood pressure
- C) Falling pressure
- D) Pulsating pressure
Answer: B) Low blood pressure
- In which vessels can waves of blood pressure or pulse be detected?
- A) Arteries
- B) Veins
- C) Capillaries
- D) Both A and C
Answer: A) Arteries
- What is the rate of blood flow in capillaries?
- A) Rapid, between 400-500mm per second
- B) Increasing from smaller to larger veins
- C) Slowest, less than 1mm per second
- D) Pulsating with heartbeat
Answer: C) Slowest, less than 1mm per second
- Which vessels have a larger bore and thick walls?
- A) Arteries
- B) Veins
- C) Capillaries
- D) Both A and C
Answer: A) Arteries
- What is the role of muscles and elastic fibers in veins?
- A) Change pulsating flow of blood
- B) Facilitate nutrient exchange
- C) Prevent backflow of blood
- D) No specific role
Answer: C) Prevent backflow of blood
- Which vessels are responsible for the exchange of gases and nutrients?
- A) Arteries
- B) Veins
- C) Capillaries
- D) Pulmonary veins
Answer: C) Capillaries