Definition
The cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO) is a type of electrical instrument that is used for showing the measurement and analysis of waveforms and other electronic and electrical phenomena. It is an extremely quick X-Y plotter that shows the input signal versus another signal or versus time. The CROs are used to analyze the waveforms, transient, phenomena, and other time-varying quantities from an extremely low-frequency variety to the radio frequencies.
Construction of CRO
The building of CRO consists of the following:
- Cathode Ray Tube
- Electronic Gun Assembly
- Deflecting Plate
- Fluorescent Screen For CRT
- Glass Envelop
Cathode Ray Tube
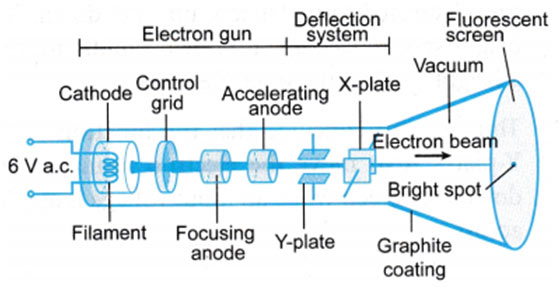
The CRO is the vacuum tube and the primary function of this gadget is to change the signal from electrical to visual. This tube consists of the electron weapon along with the electrostatic deflection plates. The primary function of this electron gun is used to generate a concentrated electronic ray that accelerates to high frequency.
The vertical deflection plate will turn the ray up and down whereas the horizontal ray moved the electron beams from the left side to the right side. These actions are autonomous from each other and therefore the ray might lie anyplace on the display.
Electronic Gun Assembly
The primary function of the electron gun is to produce the electrons to form them into a ray. This gun generally includes a heating unit, a grid, cathode, and anodes like speeding up, pre-accelerating, and focusing.
At the cathode end, the strontium and barium layers are deposited to acquire the high electrons emission of electrons at the moderate temperature level, the layers of barium, and are transferred at the end of the cathode. There are two techniques of focusing on the electron beam. These techniques are.
- Electrostatic focusing.
- Electro-magnetic focusing.
The CRO uses an electrostatic focusing tube.
Deflecting Plate
The electron beam after leaving the electron gun passes through the two sets of the deflecting plate. The pair of plate producing the vertical deflection is called a vertical deflecting plate or Y plates, and the pair of the plate which is utilized for horizontal deflection is called horizontal deflection plate or X plates.
Fluorescent Screen of CRT
In the CRT, the front face is called the faceplate, For the CRT screen, it is flat and its size is about 100mm × 100mm. The CRT screen is rather bent for bigger displays and the formation of faceplate can be done by pressing the molten glass into a form and after that heating it.
The inner face of the faceplate is covered by using phosphor crystal to alter the energy from electrical to light. Once an electronic device’s ray hits phosphor crystal, the energy level can be boosted, and thus light is produced throughout the phosphorous formation, so this occurrence is referred to as fluorescence.
Glass Envelope
It is an incredibly left cone-shaped form of construction. The inside faces of the CRT among the neck along with the display are covered through the aquadag. This is a conducting material that acts like a high-voltage electrode. The surface of the coating is connected electrically towards the accelerating anode to help the electron to be at the center.
Working of CRO
When the electron is injected through the electron gun, it passes through the control grid. The control grid controls the intensity of electrons in the vacuum tube. If the control grid has high negative potential, then it permits only a few electrons to travel through it. Hence, the dim spot is produced on the lightning screen. If the negative potential on the control grid is low, then the bright spot is produced. Thus, the intensity of light depends on the negative potential of the control grid.
After moving the control grid, the electron beam passing through the focusing and accelerating anodes. The accelerating anodes are at a high positive potential and thus they assemble the beam at a point on the screen.
After moving from the accelerating anode, the beam comes under the impact of the deflecting plates. When the deflecting plate is at zero potential, the beam produces an area at the Centre. If the voltage is applied to the vertical deflecting plate, the electron beam focuses upward and when the voltage is used horizontally the spot of light will be deflected horizontally.
Applications of CRO
While various, a CRO can be used for the following purposes:
- To identify the amplitude of a waveform.
- Comparison between the phases and frequencies of electrical signals.
- Assist procedure capacitance and inductance values.
- In the medical field and medical practice, it can be utilized for keeping an eye on different body specifications like heartbeat rates and nervous responses.
- It is likewise used for understanding the waveforms, short-term phenomenon, and other time-varying quantity from a really low-frequency range to the radio frequencies.
MCQs about Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO)
- MCQ 1: What does CRO stand for?
- A) Cathode Ray Organization
- B) Central Ray Oscilloscope
- C) Cathode Ray Oscilloscope
- D) Conductor Resistance Observation
- Answer: C) Cathode Ray Oscilloscope
- MCQ 2: What is the primary function of a Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) in a CRO?
- A) To produce electrons
- B) To convert electrical signals to visual displays
- C) To regulate the intensity of electrons
- D) To accelerate electrons to high frequency
- Answer: B) To convert electrical signals to visual displays
- MCQ 3: What is the function of the electronic gun assembly in a CRO?
- A) To control the intensity of electrons
- B) To convert electrical signals to visual displays
- C) To generate electrons and form them into a ray
- D) To deflect the electron beam
- Answer: C) To generate electrons and form them into a ray
- MCQ 4: Which focusing method does a CRO typically use?
- A) Electromagnetic focusing
- B) Magnetic focusing
- C) Electrostatic focusing
- D) Ionizing focusing
- Answer: C) Electrostatic focusing
- MCQ 5: What is the function of deflecting plates in a CRO?
- A) To generate electrons
- B) To focus the electron beam
- C) To regulate the intensity of electrons
- D) To control the horizontal and vertical deflection of the electron beam
- Answer: D) To control the horizontal and vertical deflection of the electron beam
- MCQ 6: What is the purpose of the fluorescent screen in a CRO?
- A) To regulate the intensity of electrons
- B) To convert electrical signals to visual displays
- C) To generate electrons
- D) To accelerate electrons to high frequency
- Answer: B) To convert electrical signals to visual displays
- MCQ 7: Which part of the CRO is responsible for altering the energy from electrical to light?
- A) Glass envelope
- B) Deflecting plates
- C) Cathode Ray Tube
- D) Fluorescent screen
- Answer: D) Fluorescent screen
- MCQ 8: What is the purpose of the aquadag coating inside the glass envelope of a CRO?
- A) To regulate the intensity of electrons
- B) To generate electrons
- C) To accelerate electrons
- D) To act as a high-voltage electrode
- Answer: D) To act as a high-voltage electrode
- MCQ 9: What controls the intensity of electrons in a vacuum tube of a CRO?
- A) Cathode
- B) Accelerating anodes
- C) Deflecting plates
- D) Control grid
- Answer: D) Control grid
- MCQ 10: What happens when the control grid of a CRO has a high negative potential?
- A) A dim spot is produced on the screen
- B) A bright spot is produced on the screen
- C) No spot is produced on the screen
- D) The electron beam is deflected horizontally
- Answer: A) A dim spot is produced on the screen
- MCQ 11: What does the focusing and accelerating anodes do in a CRO?
- A) Regulate the intensity of electrons
- B) Deflect the electron beam
- C) Accelerate the electron beam
- D) Convert electrical signals to visual displays
- Answer: C) Accelerate the electron beam
- MCQ 12: What happens when a voltage is applied to the vertical deflecting plate of a CRO?
- A) The electron beam moves upward
- B) The electron beam moves downward
- C) The spot of light is deflected horizontally
- D) The spot of light is deflected vertically
- Answer: D) The spot of light is deflected vertically
- MCQ 13: What is a common application of a CRO?
- A) To identify the color of a waveform
- B) To measure the weight of electrical signals
- C) To compare the phases and frequencies of electrical signals
- D) To analyze chemical reactions
- Answer: C) To compare the phases and frequencies of electrical signals
- MCQ 14: How does a CRO assist in medical practices?
- A) By measuring blood pressure
- B) By monitoring heartbeat rates and nervous responses
- C) By analyzing DNA structures
- D) By detecting viruses
- Answer: B) By monitoring heartbeat rates and nervous responses
- MCQ 15: What range of frequencies can a CRO analyze?
- A) Extremely low-frequency range only
- B) Radio frequencies only
- C) Both extremely low-frequency range and radio frequencies
- D) Microwave frequencies only
- Answer: C) Both extremely low-frequency range and radio frequencies
Wrap up!
In conclusion, the Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO) serves as a fundamental tool in electrical instrumentation, enabling the measurement and analysis of waveforms and various electronic phenomena.
Constructed with key components like the Cathode Ray Tube (CRT), Electronic Gun Assembly, Deflecting Plates, Fluorescent Screen, and Glass Envelope, the CRO efficiently converts electrical signals into visual displays for analysis.
Its working principle involves the manipulation of electron beams through control grids, focusing and accelerating anodes, and deflecting plates, resulting in the visualization of waveforms on the screen.
The applications of CRO span across multiple domains, including waveform analysis, frequency comparison, capacitance and inductance measurement, and even medical diagnostics. From low-frequency signals to radio frequencies, the CRO proves to be a versatile instrument in understanding time-varying quantities and phenomena.